Dust mites are related to spiders and scorpions and look like them too. Millions of them can live on your mattress at a time, even if you can’t see any of them with the naked eye. Dust mites can be found particularly in mattresses, carpets, and upholstery. Even though they are hard to detect and to kill, there are proactive measures you can take to prevent dust mites, and if you already have a dust mite infestation, there are still actions you can take to limit their impact and get rid of them.
Do not confuse dust mites with bed bugs. The major difference is that dust mites feed on dead human skin cells and pet dander, while bed bugs are parasites, attaching to your body and feeding on your blood. Dust mites are still dangerous too though, besides it being creepy just knowing they are in your mattress while you are sleeping. They can impact you if you have allergies or cause you to develop a new allergy. Dust mites when airborne can trigger asthma attacks, and the dust mite allergy can also trigger allergic rhinitis and eczema. Common symptoms include sneezing; runny or stuffy nose; red, itchy, or teary eyes; wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and tightness in chest; and itching.
So why are mattresses a common breeding ground for dust mites? Since humans shed 1.5 grams of dead skin cells a day and we spend a third of our lives on our mattresses, you can do the math! And by the way, just that 1.5 grams of dead skin cells each day feeds over a million dust mites a day. Yikes. As you can see, our mattresses are a playground for these little pests. Humidity and the perspiration your body causes when sleeping also contributes to the ideal dust mite habitat, warm and damp.
The best thing you can do is clean your mattress with specific techniques and pick the mattress that is best for someone with allergies. Latex mattresses tend to be a good option because they are hypoallergenic and naturally resist microbes. In fact, latex foam is also more breathable than traditional foam, trapping less heat, where a cooler environment curbs the growth and proliferation of dust mites. But whether you own a latex mattress or not, there are ways to maintain your mattress to keep it dust mite free.
Each morning, wait a while to make your bed. Yes, we just gave you permission to avoid this chore (but not for long). This gives your mattress time to air out. Every couple weeks, strip your bed entirely to let it breathe. While your at it, run the vacuum over the surface. When properly maintained, a mattress can last up to 7-10 years. If your mattress is creeping up in age, you may consider choosing a new mattress. We hate to break it to you, but if you’ve had your mattress for more than 5 years, there are most definitely dust mites, bacteria, and other microorganisms that have crept their way into your mattress layers – no matter how clean you think you are.
Your sleep health is just as important important was your overall health. Make sure your sleeping structure is helping you achieve the best sleep possible, not making you sick.
Written By Guest Blogger: Lisa Smalls

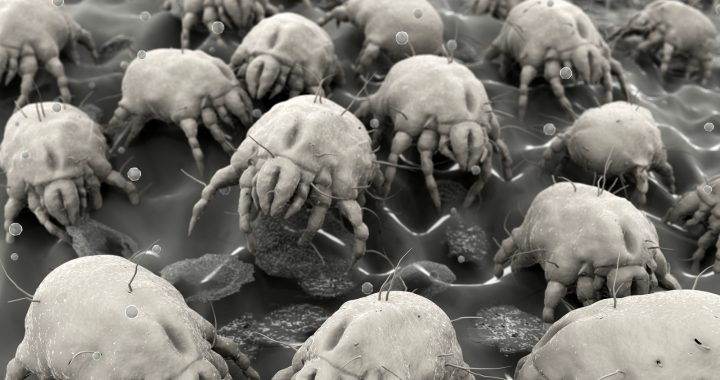

 Allergies are an overreaction of a person’s immune system to an allergen, an otherwise harmless protein that has no effect on a non-allergic person. Common sources of inhaled allergens are tree, grass and weed pollen, mold spores, dust mites, cockroaches, cats, dogs, birds, cows, horses, rabbits and rodents. The overreaction of the immune system that results from contact with one or more of these inhaled allergens may cause annoying symptoms like coughing, sneezing, itchy eyes, runny nose, and scratchy throat. A person will often have allergies to more than one allergen.
Allergies are an overreaction of a person’s immune system to an allergen, an otherwise harmless protein that has no effect on a non-allergic person. Common sources of inhaled allergens are tree, grass and weed pollen, mold spores, dust mites, cockroaches, cats, dogs, birds, cows, horses, rabbits and rodents. The overreaction of the immune system that results from contact with one or more of these inhaled allergens may cause annoying symptoms like coughing, sneezing, itchy eyes, runny nose, and scratchy throat. A person will often have allergies to more than one allergen.
